N
Nitrogen (N)
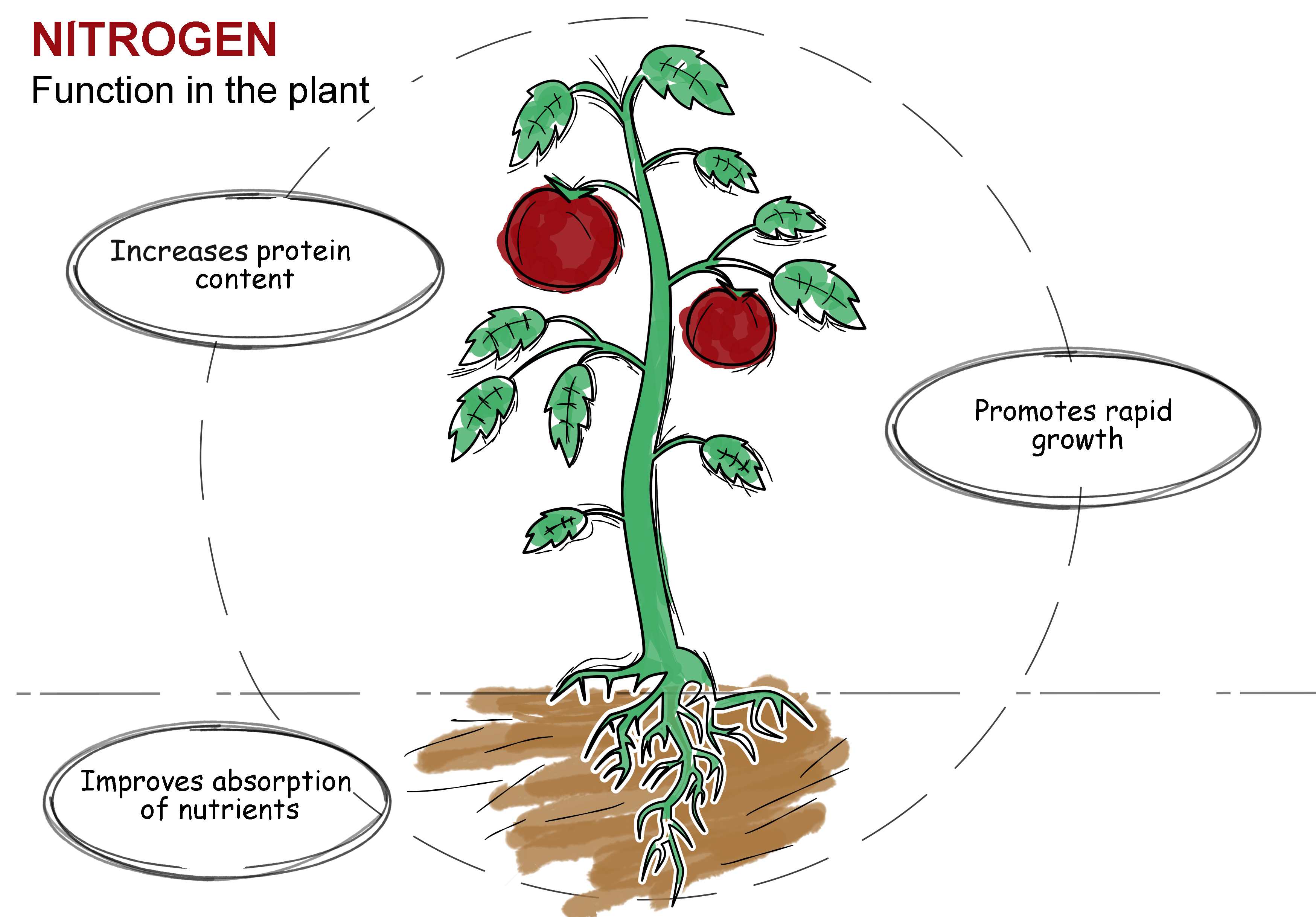
Nitrogen
NITROGEN is the most important nutrient for plant development, as it is the main element of vital biomolecules such as proteins and chlorophyll. Therefore, Nitrogen is a necessary element in all the phenological states of the plant, especially in the development of leaves and buds where there is more chlorophyll.
In the plant, Nitrogen is divided into 3 groups:
More than 50% in compounds with high molecular weight (proteins and nucleic acids); the rest as soluble organic Nitrogen (amino acids, amides, amines …) and inorganic Nitrogen (mainly nitrate and ammonium ions). Its content in the total dry weight of the plant ranges between 1.5 and 5%.
ABSORPTION
In the soil we find nitrogen, practically, in the fraction of organic N. But plants absorb it through their roots and leaves in mineral form such as ammonia nitrogen (NH4 +) and nitric nitrogen (NO3-). For this reason, the processes of mineralization of N in the soil, controlled by microorganisms, are essential.
There are genera of bacteria such as Rhizobium and Frankia that, in symbiosis with leguminous plants and other plant families, are capable of fixing atmospheric nitrogen. Ammonia, in gaseous form, can also enter the plant through the stomata. In these two processes the end result is ammonia.
CULTIFORT PRODUCTS FOR THE LACK OF NITROGEN