1. BACKGROUND
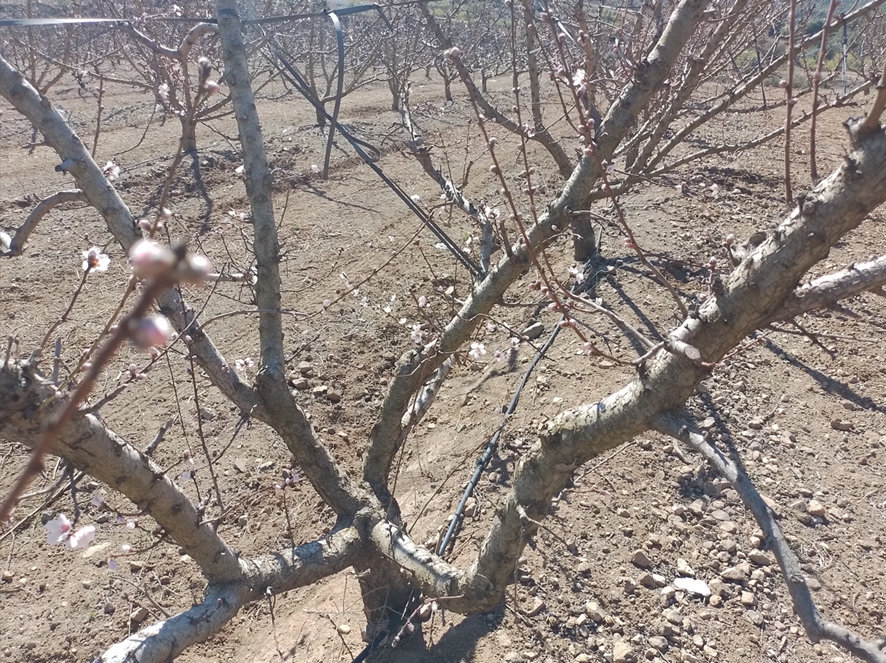
Producers of deciduous fruit trees at the European level continue to face campaigns evaluated as negative due to the lack of chilling hours for most of these species, not reaching a minimum to ensure proper hormonal regulation that guarantees normalized and homogenized processes of flowering and fruiting.
It should be noted that for proper self-regulation by the crop, a cumulative total of hours below 7 degrees Celsius must be obtained within a range between the months of December and mid-February, or by a more common practice, counting these hours from the time the trees shed their first leaves until the well-known phenological phase known as swollen bud.
However, the panorama presented to us this campaign includes frequent daytime temperatures of 20°C and not excessively low nighttime temperatures in the majority of the Iberian territory.
-
FUNCTIONAL BASES OF A COLD HOURS COMPENSATOR
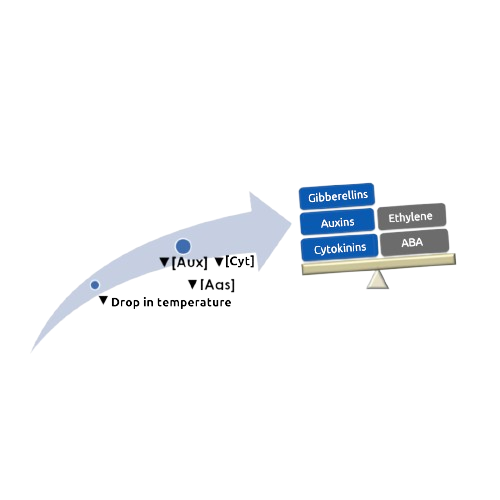
We are aware, as explained earlier, that although dormancy is related to environmental conditions, this phenomenon is of endogenous origin, meaning it is intimately connected to a progressive decrease in growth promoters (auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins) and a progressive increase in inhibitors (abscisic acid). When the concentration of these plant hormones is reversed, meaning when the endogenous content of promoters increases and the level of inhibitors decreases, dormancy is broken, and the bud sprouts. In this sense, the use of artificial substances known as “cold compensators” or currently “bud stimulators” aims to activate the enzymatic reactions involved in the synthesis of plant growth hormones that promote bud sprouting.
The function of a cold hours compensator is to stimulate chemical reactions in the buds that did not occur naturally due to the lack of low temperatures. The effect of compensators is not generalized throughout the tree since each bud typically has a different resting condition, depending on its position (terminal or lateral) and type (vegetative or floral). The application of these chemicals serves three purposes: accelerate flowering, standardize flowering, and stimulate bud sprouting.
-
CULTIFORT SOLUTIONS
From CULTIFORT, a strategy with proven results is offered with a compensating effect for cold hours or bud-stimulating effect.
This strategy is based on the combination of BVC 2021 and FASKOLOR.
BVC 2021 is a biostimulant with a combined action of specifically selected amino acids, nitrogen, and reducing sugars to exert a versatile influence on different phenological phases, promoting the self-synthesis of natural substances (proteins, peptides, amino acids, phytohormones such as cytokinins) and improving the profiles of active substances (polyphenols, essential oils, alkaloids, vitamins…).
Its cytokinin-promoting activity will enhance, among other variables:
- Promotion of the onset of plant physiological activity.
- Stimulation of leaf and flower formation.
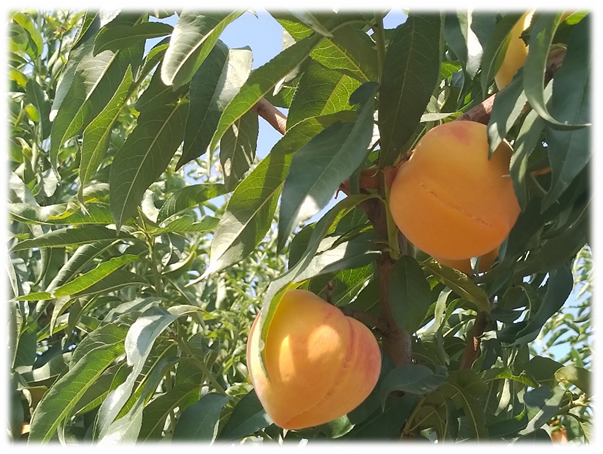
- Improvement in fruit quality.
- Promotion of precocity in the maturation phase.
- Increased resistance to low temperatures and adverse weather conditions, a key factor for flowering and fruiting phenologies.
On the other hand, FASKOLOR incorporates organic acids and peptidic complexes that exert a physiological, non-hormonal action on the crop. It acts directly on the chloroplast, maintaining the structure and function of thylakoidal membranes and regulating the level of oxidation products and redox balances.
-
RESULTS OF THE PROPOSED STRATEGY.
Number of applications: 3 spread applications.
- First application at pink bud stage (BVC 2021 foliar + FASKOLOR root).
- Second application between 75-85% open flower (BVC 2021 foliar + FASKOLOR root).
- Third application at the beginning of fruit color change (BVC 2021 foliar + FASKOLOR root).