Zn
Zinc (Zn)
Zinc
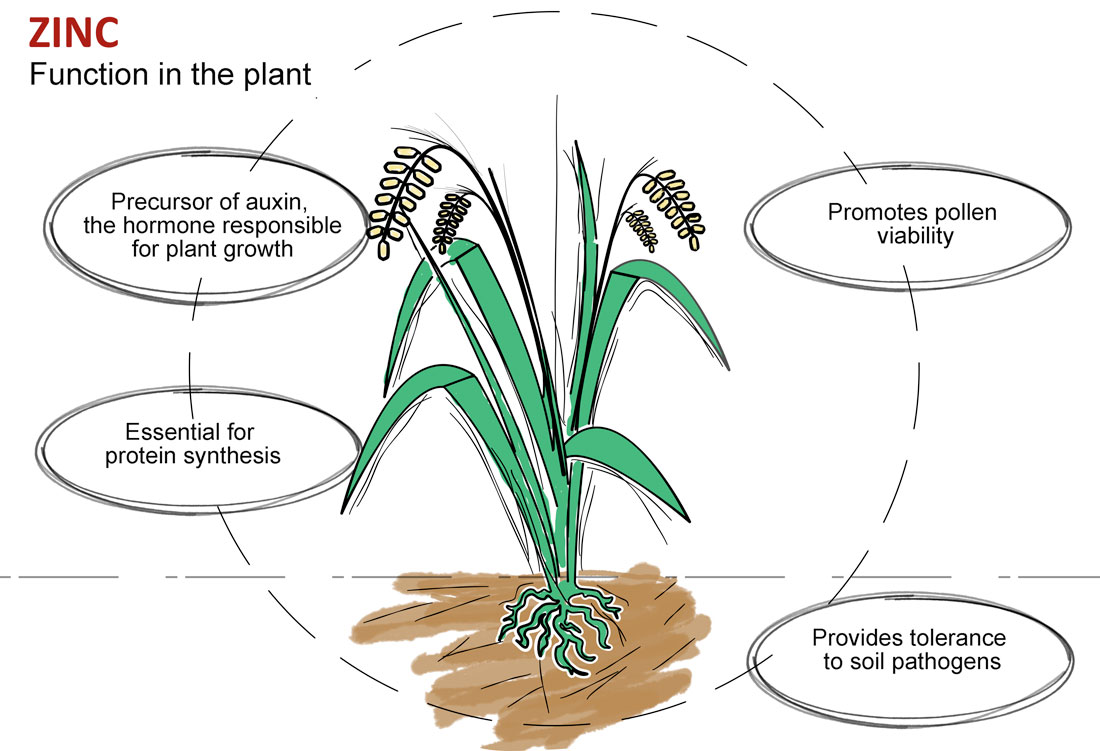
Zinc is an essential microelement that serves as an enzymatic cofactor of at least 80 enzymatic systems of important plant metabolic processes.
On one hand, in photosynthesis plays an important role in the transformation of sugars into starch, the main reserve substance of the plant.
Zinc contributes in the synthesis of tryptophan, the amino acid previous to auxin, the hormone responsible for plant growth.
In protein synthesis, it is involved in the stabilization of ribosomes and forming a structural part of RNA polymerase.
During ripening and seed production, zinc promotes pollen formation and viability, which translates into better grain yield.
Zinc also gives plants resistance to soil pathogens.
ABSORPTION
Zinc is absorbed as Zn+2 ion, more commonly as a chelate. Its availability is higher in soils with acidic pH.
DEFICIENCIES
The characteristic symptoms of Zinc deficiency are the internervial discoloration of the middle section of the plant, decrease in leaf growth and shortening of internodes, causing plant dwarfism. These symptoms are easy to detect in corn, sorghum and fruit trees
CULTIFORT PRODUCTS FOR THE LACK OF ZINC